3 min read
5 Data Center Construction Challenges Solved With HyperCool®
Newly constructed data centers and AI factories must be carefully designed to respect dramatic increases in thermal output from today’s superchips....
3 min read
 Arnon Cohen
:
Nov 8, 2024 8:41:12 AM
Arnon Cohen
:
Nov 8, 2024 8:41:12 AM

Hyperscale data centers are contending with an unprecedented surge in heat output driven by powerful AI chips and dense workloads. According to a recent International Energy Agency (IEA) report, data centers’ total electricity consumption could reach more than 1,000 terawatt-hours (TWh) in 2026 — more than double the 460 terawatt-hours (TWh) of consumption that was tracked in 2022.
As these workloads grow, so does the need to manage the associated heat. Success for AI factories and data centers hinges on heat rejection, dissipation, and reuse. The right innovative cooling solutions can even turn heat from a costly byproduct into a financial and environmental asset.
Cooling energy-intensive chips like the NVIDIA Grace Blackwell is just the beginning for hyperscale data center companies. The most effective cooling solutions will also optimize every watt used in the data center to reduce costs, improve sustainability, and ensure consistent, reliable performance. Hyperscalers can utilize a few strategic technologies to manage today’s relentless data center heat load:
These solutions use cooling mechanisms like fans or liquid cooling within the server rack to actively draw heat away from its components. The heat is dispersed safely within the facility to prevent hotspots, which can undermine performance. Dissipation systems provide the initial cooling that occurs at the micro-level within individual servers and racks.
This category includes cooling systems that move excess heat away from high-density chips to prevent damage and reduce cooling requirements. The heat is ultimately transferred from the cooling system to the outside environment. Rejection systems operate at the macro-level, where the entire data center cooling system is considered.
Reuse technology captures data center waste heat and repurposes it for other uses, such as heating nearby buildings or powering facility processes. Heat reuse reduces the overall energy footprint of the data center, aligning with sustainability efforts and lowering operational costs by turning waste into a valuable resource. Repurposing waste heat can both reduce energy consumption (a financial boon) and contribute to corporate sustainability goals.
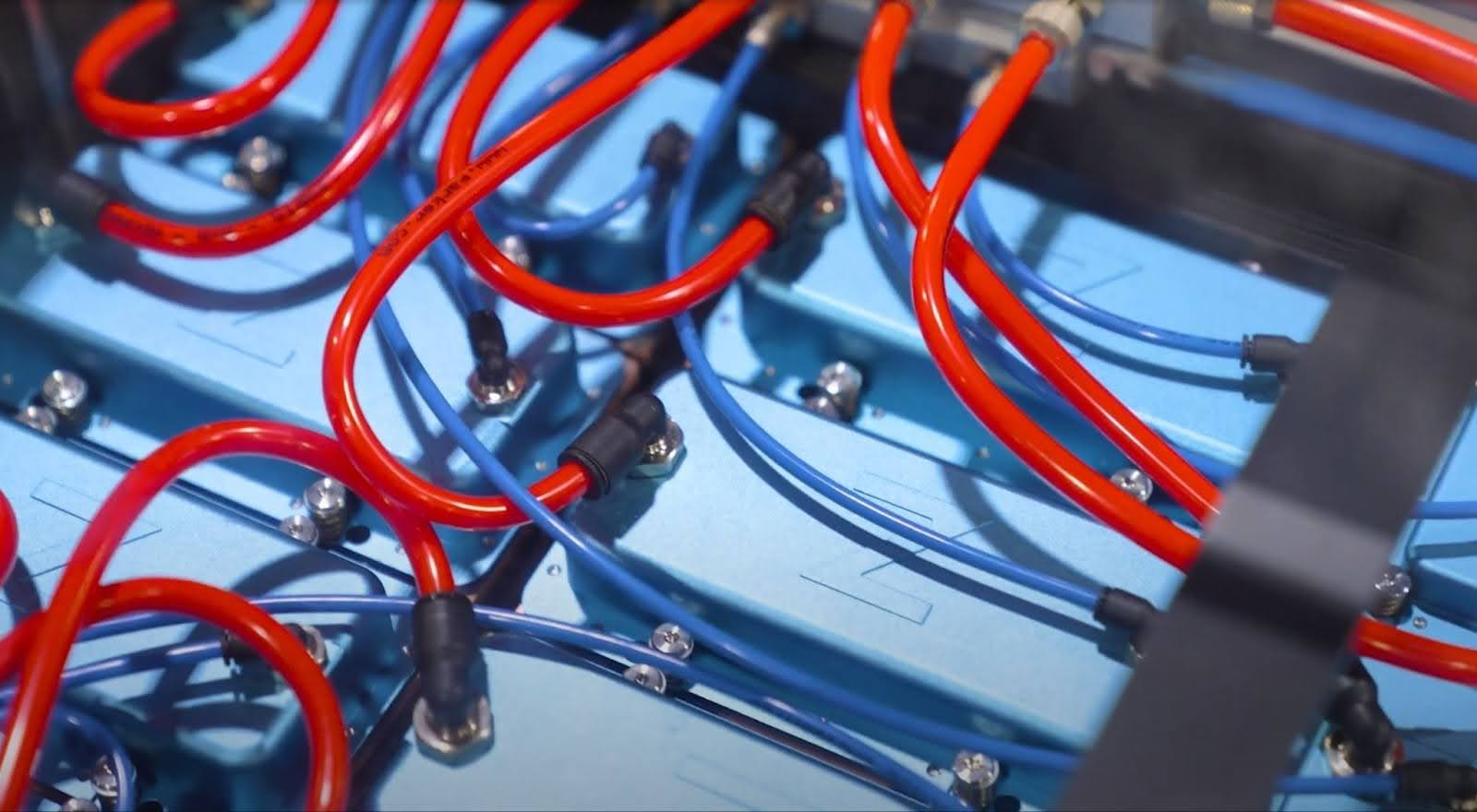
Hyperscale data centers have turned to HyperCool® from ZutaCore® for a cutting-edge approach to heat management with direct-to-chip, waterless liquid cooling. Designed to handle even the most intense heat loads, the HyperCool Cooling Distribtuion Unit (CDUs) are engineered for ultimate flexibility and reliability in demanding environments.
Here’s how it works:
Hyperscale data center operators can balance the demands of heat management with green initiatives using the robust, flexible, and sustainable HyperCool system from ZutaCore. Efficient heat dissipation, innovative heat reuse, and flexible deployment options ensure reliable data center operation while also providing a pathway to energy-efficient, environmentally responsible growth.
To learn more about how ZutaCore is transforming heat management in hyperscale data centers, explore our recent applications in the field or watch our technology in action.
3 min read
Newly constructed data centers and AI factories must be carefully designed to respect dramatic increases in thermal output from today’s superchips....

3 min read
As high-performance computing (HPC), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) workloads continue to drive up power densities in modern...
1 min read
As AI superchips push the boundaries of power and performance, the heat they generate is becoming a critical challenge for data centers. With...